accuracy and precision in chemistry|accuracy and precision calculator : iloilo Accuracy is a measure of how close a measurement is to the correct or accepted value of the quantity being measured. Precision is a measure of how close a series of . Tingnan ang higit pa 3, 2, 0, -1/2 The quantum numbers for Ni (electron #28) are: Principal = 3 (because the electron is in energy level 3) Angular = 2 (because the electron is in a d sublevel) Magnetic = 0 (because the electron is in the middle orbital of the 5 orbitals in the 3d sublevel) Spin = -1/2 (because the electron is down spin() Here is a video to provide .
PH0 · precision vs accuracy chemistry examples for kids
PH1 · precision calculator chemistry
PH2 · precise vs accurate chem
PH3 · difference between precision and accuracy
PH4 · chemistry precision and accuracy calculator
PH5 · accurate and precise chemistry examples
PH6 · accuracy and precision difference chemistry
PH7 · accuracy and precision calculator
PH8 · Iba pa
No more having to learn each Schema type, which elements are required vs. recommended or worrying about errors and issues. Schema.dev's Schema Builder makes it as simple as point and click to generate the perfect JSON-LD structured data for dozens of Google supported Schema types! and all for FREE!
accuracy and precision in chemistry*******In everyday speech, the terms accuracy and precision are frequently used interchangeably. However, their scientific meanings are quite different. Accuracy is a measure of how close a measurement is to the correct or accepted value of the quantity being measured. Precision is a measure of . Tingnan ang higit paThis action is not available. How do professional basketball players improve their shooting accuracy? Basketball is one of those . Tingnan ang higit paAccuracy is a measure of how close a measurement is to the correct or accepted value of the quantity being measured. Precision is a measure of how close a series of . Tingnan ang higit paAccuracy and Precision. Scientists typically make repeated measurements of a quantity to ensure the quality of their findings and to evaluate both the precision and the accuracy of .
Accuracy and precision are very similar in the fact, that they both refer to measurement quality, but they are very different indicators of .
Precision. The precision is a measure of how closely grouped the individual values are around the average value. A common way to express precision is through the .
Accuracy and Precision Video. Accuracy and precision are the two important terminologies used in any measurement. These two terms describe how closely a measurement resembles a standard or .Accuracy and Precision. Scientists typically make repeated measurements of a quantity to ensure the quality of their findings and to know both the precision and the accuracy of their results. .There are two concepts we need to understand in experimental error, accuracy and precision. Accuracy is how close your value or measurement is to the correct (true) . Accuracy is how close a value is to its true value. An example is how close an arrow gets to a bull's-eye center. Precision is how repeatable a measurement is. An example is. Both accuracy and precision are the goal of any measurement. Variations in accuracy and precision are largely controllable. In target shooting, you improve accuracy by moving .accuracy and precision in chemistryUnderstanding Accuracy and Precision. In experimentation, it’s important to remember what we mean by accuracy and precision. Accuracy is how close your value is to the true value. The problem is . Importance of accuracy and precision in chemistry. As an analytical chemistry weight balance expert, I understand the importance of accuracy and precision in chemistry. Accuracy and precision are critical components of scientific measurement, and they play a crucial role in ensuring the quality and reliability of chemical analysis. .
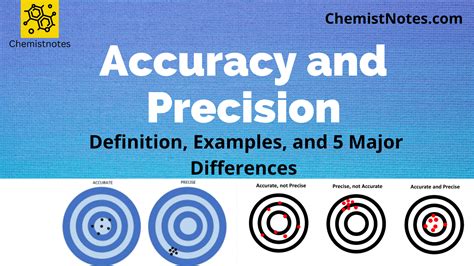
In analytical chemistry, accuracy and precision are two critical concepts that are often confused with each other. This article explains the difference between accuracy and precision in analytical chemistry and provides examples to help clarify the distinction. Additionally, it addresses frequently asked questions (FAQs) about accuracy and . A measurement is considered accurate if it yields a result that is very close to the true or accepted value. Precise values agree with each other; accurate values agree with a true value. These characterizations can be extended to other contexts, such as the results of an archery competition (Figure 1.5.2 1.5. 2 ).In experimentation, it’s important to remember what we mean by accuracy and precision. Accuracy is how close your value is to the true value. The problem is you can’t always know what the actual value is. If you’re in a lab for a chemistry course, chances are the instructor or TA knows the value you should get and can let you know how .Accuracy is the quality that a measurement has if it is close to some other quantity’s true value. Precision shows how much a repeated measurement will change its value. For example, if several darts were thrown at a dart board, and all hit the same spot far away from the bull’s-eye, we could say the throws were precise, but inaccurate. If the darts .
Results for dispenser #2 represent improved accuracy (each volume is less than 3 mL away from 296 mL) but worse precision (volumes vary by more than 4 mL). Finally, she can report that dispenser #3 is working well, dispensing cough syrup both accurately (all volumes within 0.1 mL of the target volume) and precisely (volumes differing from each . The quarter weighs about 6.72 grams, with a nominal uncertainty in the measurement of ± 0.01 gram. If we weigh the quarter on a more sensitive balance, we may find that its mass is 6.723 g. This means its mass lies between 6.722 and 6.724 grams, an uncertainty of 0.001 gram. Every measurement has some uncertainty, which depends on . This chemistry video tutorial explains the difference of accuracy and precision in measurement. This video gives an example of four students attempting to m. A measurement is considered accurate if it yields a result that is very close to the true or accepted value. Precise values agree with each other; accurate values agree with a true value. These characterizations can be extended to other contexts, such as the results of an archery competition (Figure 1.6.2 1.6. 2 ).
Figure 1.4.1 1.4. 1: To measure the volume of liquid in this graduated cylinder, you must mentally subdivide the distance between the 21 and 22 mL marks into tenths of a milliliter, and then make a reading (estimate) at the bottom of the meniscus. Refer to the illustration in Figure 1.4.1 1.4. 1. The darts are grouped together and have hit the bulls-eye. This demonstrates high precision and high accuracy. Scientists always strive to maximize both in their measurements. Figure \(\PageIndex{3}\): Students in a chemistry lab are making careful measurements with a series of volumetric flasks. Accuracy and precision are .accuracy and precision calculatorExcept where otherwise noted, this page is adapted by JR van Haarlem and Samantha Sullivan Sauer from “1.5 Measurement Uncertainty, Accuracy, and Precision” In General Chemistry 1 & 2 by Rice University, a derivative of Chemistry (Open Stax) by Paul Flowers, Klaus Theopold, Richard Langley & William R. Robinson and is licensed under .
Therefore, Device B has the best combination of accuracy and precision. Errors in general chemistry are classified as systematic (determinate) and random (indeterminate). . When using the CRC Handbook of Chemistry and Physics notice that the units are kg∙m-3, which is the same as kg/m 3. You will need to convert to g/mL.
This demonstrates poor precision, but fairly high accuracy. This situation is not desirable in a lab situation because the “high” accuracy may simply be random chance and not a true indicator of good measuring skill. The darts are grouped together and have hit the bulls-eye. This demonstrates high precision and high accuracy.
A measurement is considered accurate if it yields a result that is very close to the true or accepted value. Precise values agree with each other; accurate values agree with a true value. These characterizations can be extended to other contexts, such as the results of an archery competition (Figure 1.5.2 1.5. 2 ).
CHEM 107 General Chemistry for Applied Sciences 1: Essential Ideas of Chemistry 1.5: Measurement Uncertainty, Accuracy, and Precision . Suppose a quality control chemist at a pharmaceutical company is tasked with checking the accuracy and precision of three different machines that are meant to dispense 10 ounces (296 mL) of cough syrup into .accuracy and precision in chemistry accuracy and precision calculator Accuracy and Precision. FlexBooks 2.0 >. CK-12 Chemistry for High School >. Accuracy and Precision. Written by: Ck12 Science. Fact-checked by: The CK-12 Editorial Team. Last Modified: Jul 12, 2021.Accuracy and Precision. Scientists typically make repeated measurements of a quantity to ensure the quality of their findings and to know both the precision and the accuracy of their results. Measurements are said to be precise if they yield very similar results when repeated in the same manner. . Chemistry. Provided by: OpenStax College .
Configure o dispositivo Roku na sua TV. Para mais informações, . Insira o seu e-mail e senha da Conta Globo, se não estiver logado no Globoplay; Insira o código que está na tela da sua TV e clique em "Ativar". globo.com. g1; globoesporte; gshow; famosos & .
accuracy and precision in chemistry|accuracy and precision calculator